“High-pressure behavior of otavite (CdCO3)”
- Authors
R. Minch, D. Seoung, L. Ehm, B. Winkler, K. Knorr, L. Peters, L.A. Borkowski, J.B. Parise, Y. Lee, L. Dubrovinsky, W. Depmeier
- Journal
Journal of Alloys and Compounds
Vol.508, pp.251-257, 2010.10 - DOI
Abstract
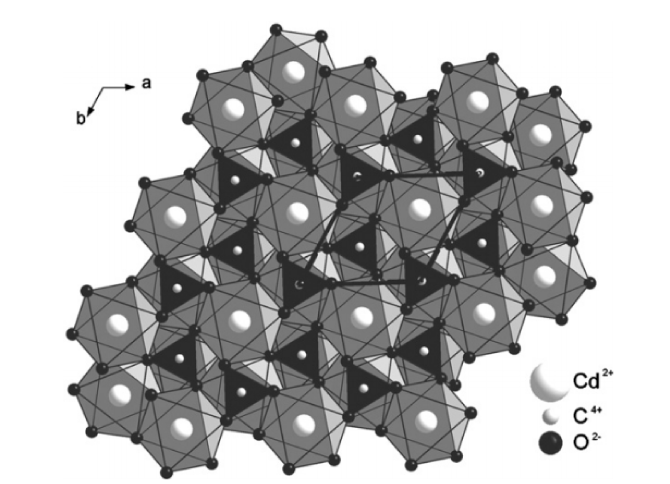
The high-pressure, room temperature behavior of otavite (CdCO3) was investigated by angle-dispersive synchrotron radiation powder diffraction up to 40 GPa, Raman spectroscopy up to 23 GPa and quantum mechanical calculations based on density functional theory. The calcite-type structure of CdCO3 is stable up to at least ∼19 GPa as shown by Raman spectroscopy. The compression mechanism was obtained from structure refinements against the diffraction data. The quantum mechanical calculations propose a calcite–aragonite phase transition to occur at about 30 GPa. The existence of a pressure-induced phase transition is supported by the Raman and diffraction experiments. Evidence for the transformation is given by broadening of X-ray reflections and external Raman bands starting from about 19 GPa in both experiments.